How much do you know about copper clad laminate (CCL)? Let me explain.
2025-09-10
How much do you know about copper clad laminate (CCL)? Let me explain.
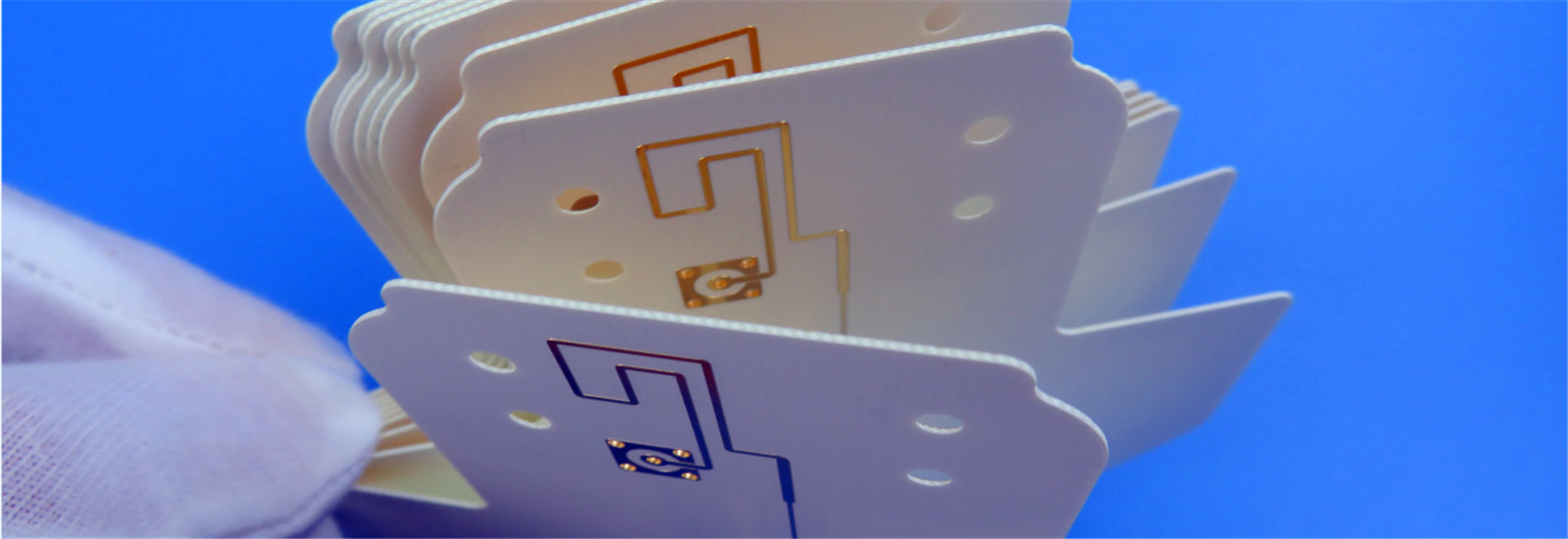
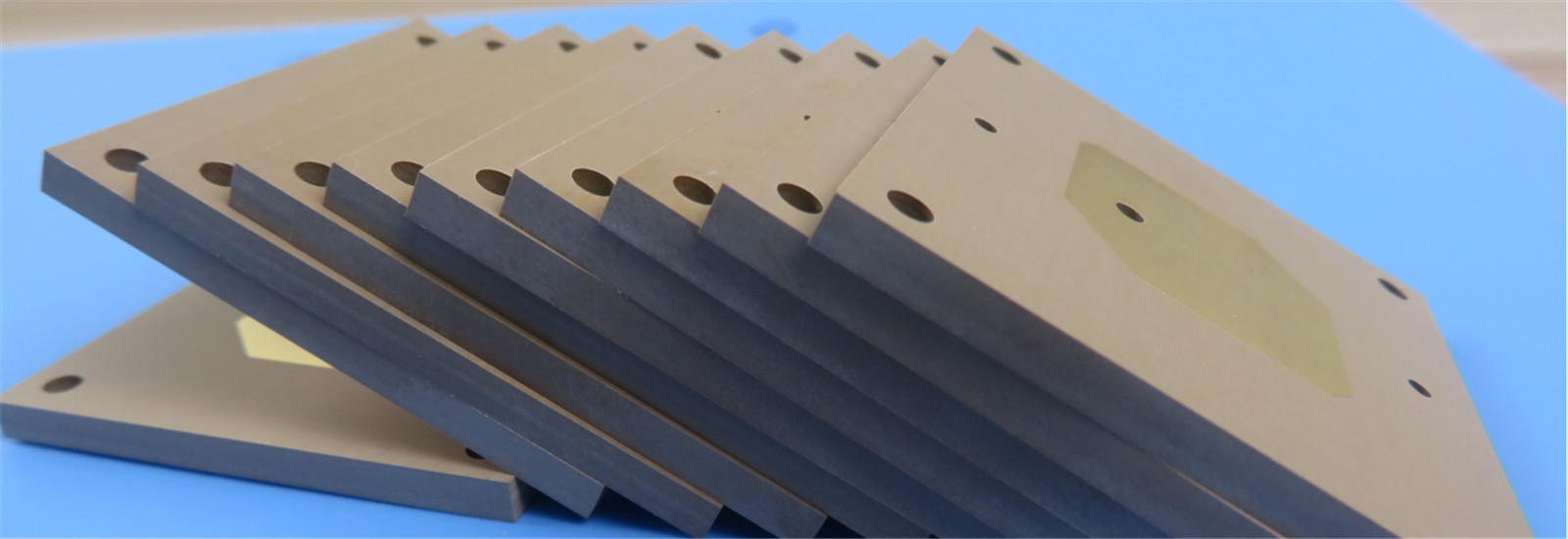
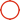
Copper clad laminate (CCL) is the core substrate for PCBs, with downstream applications in communications, computers, automotive, industrial, and medical fields. Its upstream suppliers include raw materials such as copper foil, resin, and glass fiber, while its downstream suppliers include PCB manufacturers and end-use electronic product manufacturers. This industry is highly cyclical and is entering a new growth cycle, driven by emerging demands such as 5G, AI servers, and automotive electronics.
CCL is a sheet material made by hot-pressing a reinforcing material impregnated with resin, coated on one or both sides with copper foil, and then hot-pressed. It fulfills the three main functions of conducting electricity, insulating, and supporting printed circuit boards, making it a core material for PCB manufacturing.
The CCL industry chain has a clear three-tier structure: upstream raw material supply (copper foil, glass fiber cloth, resin, filler, etc.), midstream CCL manufacturing, and downstream PCB applications.
The three core raw materials for CCL are copper foil, resin, and glass fiber cloth, accounting for 42%, 26%, and 19% of the cost, respectively, for a total of 87%.
If you require additional substrates, please feel free to contact us! Bicheng Company specializes in providing high-frequency circuit boards and raw materials.
View More
[Hotspot] Global PCB output value grows steadily, and AI capital expenditure heats up the underlying material track
2025-07-16
On July 8, the PCB concept was hot. According to Prismark statistics, the global PCB output value is expected to grow to US$94.7 billion in 2029. The CAGR from 2024 to 2029 will reach 5.2%; the PCB output value of the Chinese market will reach US$49.7 billion in 2029.
In addition, in 2025, the capital expenditure of cloud factories such as Microsoft and Google will increase by more than 30% year-on-year. The capital expenditure of China's Alibaba and Tencent is expected to exceed 120 billion/80 billion yuan, and the demand for AI infrastructure will drive the accelerated expansion of the production capacity of underlying materials such as PCB.
The AI-driven technological innovation upcycle will last longer and generate greater market demand. China's PCB industry continues to upgrade and expand mid-to-high-end production capacity and deploy overseas production capacity, and its performance release is sustainable.
The overall demand for downstream electronics is currently showing a recovery trend, coupled with the continued upward momentum in innovative fields represented by AI and high-speed communications, which together support the growth in overall PCB demand. With the iteration of AI hardware performance, PCB will be further upgraded to higher specifications in terms of product technology and materials. Relying on its early technological accumulation and improved product competitiveness, Bicheng Technology has gradually improved its industry position in the high-end market, and its AI PCB supply share has continued to increase. Bicheng is expected to achieve rapid development by seizing the opportunities of AI development.
===================================================================================
Copyright statement: The copyright of the information in this article belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of this platform. It is for sharing only. If there are copyright and information errors involved, please contact us to correct or delete it. Thanks!
View More
Wangling's F4B insulation material
2025-06-13
Taizhou Wangling Insulation Material Factory was established in 1982. Its products are mainly high-frequency microwave materials, with 6 product series:
1. PTFE glass fiber cloth coated substrate F4B series, DK value 2.2~6.15 optional;
2. Microwave composite dielectric substrate TP/TF series, DK value 3.0~25 optional;
3. Organic polymer ceramic filled substrate WL-CT series, DK value 3.0, 3.38, 3.48, 4.4, 6.15;
4. PTFE quartz ultra-thin ultra-fine glass fiber cloth ceramic filled substrate F4BTMS series, DK value 2.2, 2.55, 2.65, 2.94, 3.0, 3.5, 4.5, 6.15, 10.2;
5. PTFE ceramic composite substrate TFA series, DK value 2.94, 3.0, 6.15, 10.26. Insulation cloth, anti-stick paint cloth.
The company has passed ISO quality management system certification and J engineering three certificates. It has been successfully supported by national key projects for many times, and has been commended by the national aerospace, aviation and manned space projects, and won the title of Outstanding Supplier of China's Aerospace. The products are widely used in aerospace, aviation, satellite communications, navigation, radar, infrastructure, electronic countermeasures, 3G, 4G, 5G communications, Beidou satellite system, mobile Internet, etc.
===================================================================================
Copyright statement: The copyright of the information in this article belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of this platform. It is for sharing only. If there are copyright and information errors involved, please contact us to correct or delete it. Thanks!
View More
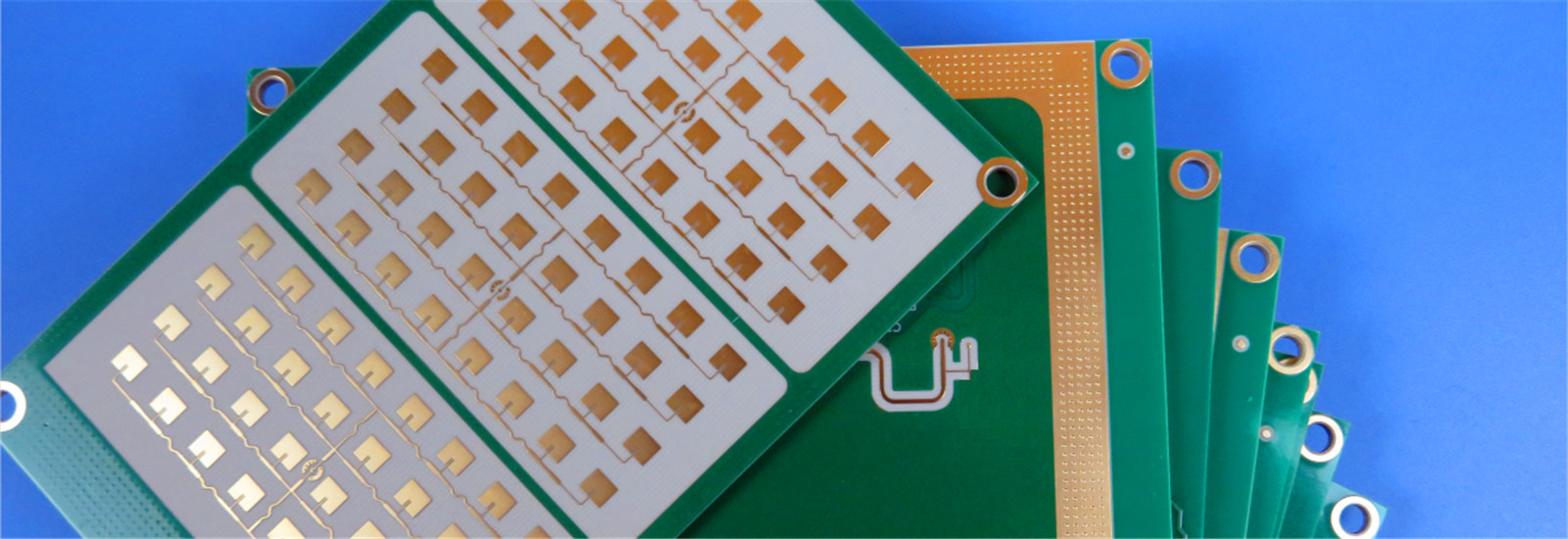
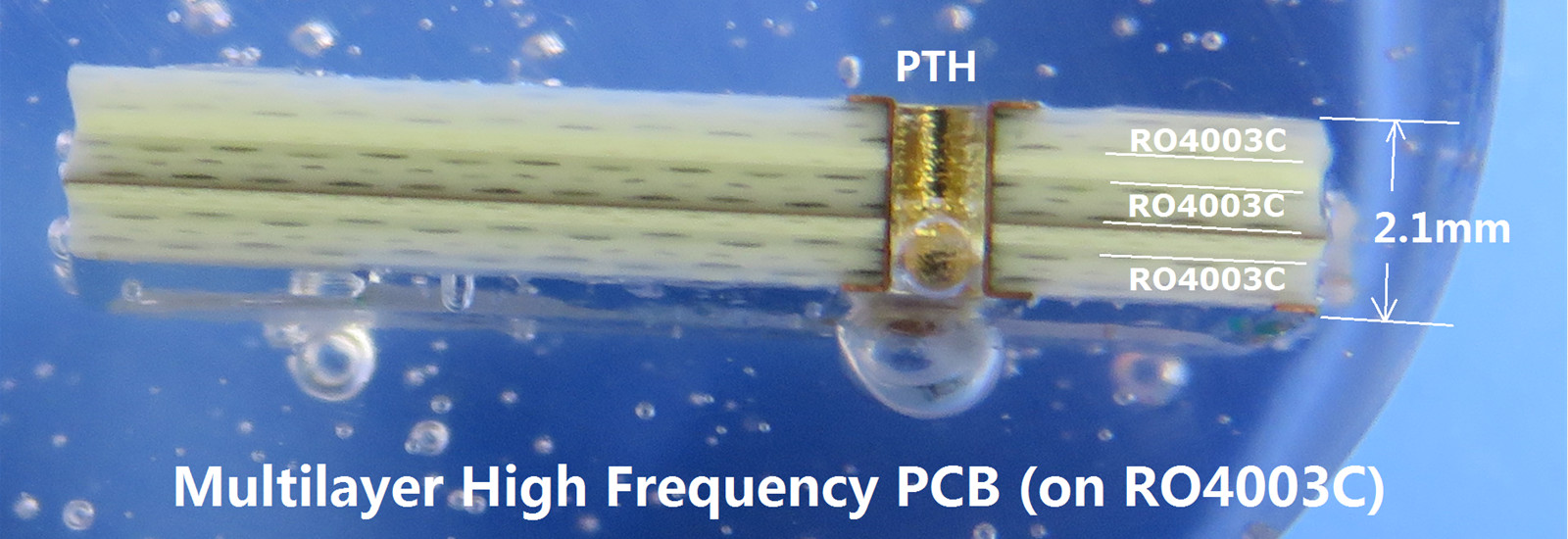
What are the important parameters of high-speed and high-frequency PCB boards?
2025-05-09
The production process of high-speed and high-frequency PCB boards is basically the same as that of ordinary PCB boards. The key point to achieve high frequency and high speed lies in the properties of raw materials, that is, the characteristic parameters of raw materials. The main material of high-speed and high-frequency PCB boards is high-frequency and high-speed copper-clad boards. The core requirement is to have low dielectric constant (Dk) and low dielectric loss factor (Df). In addition to ensuring low Dk and Df, the consistency of Dk parameters is also one of the important factors to measure the quality of high-speed and high-frequency PCB boards. In addition, another important parameter is the impedance characteristics of the PCB board and some other physical properties.
The dielectric constant (Dk) of the high-frequency and high-speed PDB board substrate must be small and stable. Generally speaking, the smaller the better. The signal transmission rate is inversely proportional to the square root of the material dielectric constant. High dielectric constants are prone to cause signal transmission delays.
The dielectric loss (Df) of the substrate material of high-frequency and high-speed PCB boards must be small, which mainly affects the quality of signal transmission. The smaller the dielectric loss, the smaller the signal loss.
The impedance of high-frequency and high-speed PCB boards actually refers to the parameters of resistance and reactance. Impedance control is the most basic principle for our high-speed design, because PCB circuits must consider the installation of electronic components, and after the installation, the conductivity and signal transmission performance must be considered. Therefore, the lower the impedance, the better. Generally, major board manufacturers will ensure a certain degree of impedance error during PCB processing.
===================================================================================
Copyright statement: The copyright of the information in this article belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of this platform. It is for sharing only. If there are copyright and information errors involved, please contact us to correct or delete it. Thanks!
View More
Commonly used PCB boards in antenna design
2025-04-30
In antenna design, the commonly used PCB boards are as follows:
FR-4: low cost, good mechanical strength and insulation performance, relative dielectric constant is generally between 4.0 - 4.5. Suitable for general wireless communication equipment antennas, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and other short-distance communication antennas. It is more suitable for cost-sensitive applications with not particularly high performance requirements.
Rogers: has a low dielectric constant and loss tangent, which can effectively reduce signal transmission loss. Different models of Rogers board dielectric constants can be selected between 2.2 - 10 to meet different design requirements. Commonly used in high-frequency antenna design, such as millimeter wave antennas, satellite communication antennas and other wireless communication systems with high signal quality requirements. Common ones include Rogers 5880, Rogers 3003, Rogers 4350B, etc., and there is also Rogers 5880LZ low dielectric constant series.
Taconic: Taconic sheets have a lower dielectric constant, which can reduce the delay and distortion of signal propagation and facilitate the transmission of high-frequency signals. The dielectric constants of different models vary. Some common models have a dielectric constant between 2 and 5, which are suitable for applications in high-frequency bands such as millimeter waves. Among them, TLY-5 is made of very light cloth-textured glass fiber, which has the advantages of dimensional stability, low dissipation factor, low moisture absorption rate, high copper peel strength, and uniform dielectric constant. It can be used in automotive radar, satellite/cellular communications, power amplifiers, LNB, LNA, LNC, and Ka, E and W bands. RF-35™ is also a common model on the market and is suitable for various high-frequency applications.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sheet: The dielectric constant is stable, usually between 2.0 and 3.0. The loss is very low, suitable for high-frequency signal transmission. It is often used in high-precision, high-performance antenna design, such as radar antennas, antennas in the aerospace field, and high-frequency RF circuits.
Ceramic-filled sheet: The dielectric constant can be adjusted according to different ceramic filling ratios. It has high mechanical strength and heat resistance. It can reduce costs to a certain extent while maintaining good performance. It is suitable for medium and high frequency antenna design, such as 5G communication antennas, and miniaturized antennas with specific requirements for size and performance.
Wangling sheet: Domestic sheet, commonly used types such as polytetrafluoroethylene glass fiber cloth copper clad laminate series F4BM, F4BME, polytetrafluoroethylene glass fiber cloth ceramic filled copper clad laminate series F4BTM, F4BTME. In addition, the dielectric constant of the composite dielectric substrate series TP and TF can be controlled at 3.0~25, and has the characteristics of low tangent loss and low temperature drift. It should be noted that when PCB board factories use Wangling boards for processing, certain process problems may occur because they have never processed similar boards before.
===================================================================================
Copyright statement: The copyright of the information in this article belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of this platform. It is for sharing only. If there are copyright and information errors involved, please contact us to correct or delete it. Thanks!
View More